Abstract
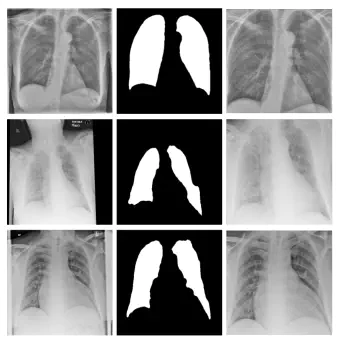
During the COVID-19 pandemic, the sheer volume of imaging performed in an emergency setting for COVID-19 diagnosis has resulted in a wide variability of clinical CXR acquisitions. This variation is seen in the CXR projections used, image annotations added and in the inspiratory effort and degree of rotation of clinical images. The image analysis community has attempted to ease the burden on overstretched radiology departments during the pandemic by developing automated COVID-19 diagnostic algorithms, the input for which has been CXR imaging. Large publicly available CXR datasets have been leveraged to improve deep learning algorithms for COVID-19 diagnosis. Yet the variable quality of clinically-acquired CXRs within publicly available datasets could have a profound effect on algorithm performance. COVID-19 diagnosis may be inferred by an algorithm from non-anatomical features on an image such as image labels. These imaging shortcuts may be dataset-specific and limit the generalisability of AI systems. Understanding and correcting key potential biases in CXR images is therefore an essential first step prior to CXR image analysis. In this study, we propose a simple and effective step-wise approach to pre-processing a COVID-19 chest X-ray dataset to remove undesired biases. We perform ablation studies to show the impact of each individual step. The results suggest that using our proposed pipeline could increase accuracy of the baseline COVID-19 detection algorithm by up to 13%.