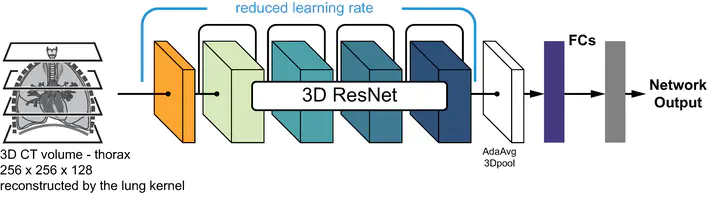
Abstract
In this study, the long-term mortality in the National Lung Screening Trial (NLST) was investigated using a deep learning-based method. Binary classification of the non-lung-cancer mortality (i.e. cardiovascular and respiratory mortality) was performed using neural network models centered around a 3D-ResNet. The models were trained on a participant age, gender, and smoking history matched cohort. Utilising both the 3D CT scan and clinical information, the models can achieve an AUC of 0.73 which outperforms humans at cardiovascular mortality prediction. By interpreting the trained models with 3D saliency maps, we examined the features on the CT scans that correspond to the mortality signal. The saliency maps can potentially assist the clinicians’ and radiologists’ to identify regions of concern on the image that may indicate the need to adopt preventative healthcare management strategies to prolong the patients’ life expectancy.